前言
上一篇文章已经学习了使用 SSH 连接越狱设备,以及利用 Clutch, class-dump 等工具进行砸壳和导出头文件的操作。 本篇文章会在上一篇文章的基础上再一点运行时的分析,所以,需要先复习一下功课啦。
Cycript 运行时分析
什么是 Cycript
Cycript 糅合了 ES6, Objective-C++ 与 Java 等语法风格的脚本语言,是作为一个 Cycript-to-JavaScript 编译器的实现,并且使用了(未修改)的 JavaScript 内核作为其虚拟机。Cycript 主要被用于 iOS 的逆向工程。
安装 Cycript
越狱设备安装 Cycript 可以在官网下载 SDK,然后再推送到越狱设备上。但比较方便的方法是在 Cydia 里搜索并下载。
玩起来
上一篇说到从 App Store 下载应用都是经过签名加密的,并且利用 Clutch 砸壳得到解密后的 ipa 包,那这次试一下在助手市场下载应用进行头文件导出的操作。 以美图秀秀为例,在助手市场下载之后进入应用存储目录,查找美图秀秀存储的目录。
iOS 常用的文件目录:
- home ~ 目录 /var/root
- 应用存储目录 /var/mobile/Containers/Bundle/Application
- 照片存储目录 /private/var/mobile/Media/DCIM
- 命令存储目录 /usr/bin
进入 /var/mobile/Containers/Bundle/Application 目录,ls 子目录,找到美图秀秀的存储位置。
NY:/var/mobile/Containers/Bundle/Application root# ls 8D71E631-48D6-4FE6-A8BE-5394AD898DD7/ |
Mach-O 文件
直接进入 MTXX.app 目录下,将二进制可执行文件 MTXX 直接 scp 推到 Mac 上。 在 OS X 和 iOS 操作系统下的二进制可执行文件为 Mach-O 文件,可以利用 otool 命令查看。
- 查看 Mach-O 头
➜ Reverse otool -h MTXX |
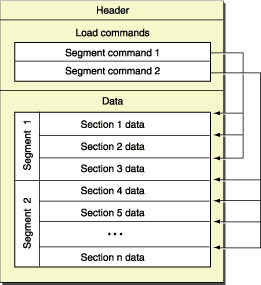
Mach-O 为 Mach Object 文件格式的缩写,它是一种用于可执行文件,目标代码,动态库,内核转储的文件格式。作为a.out格式的替代,Mach-O 提供了更强的扩展性,并提升了符号表中信息的访问速度。
一个 Mach-O 文件包含三个最主要的部分:
-
在每个 Mach-O 文件的开头是 Header ,用来标识这个文件是 Mach-O 文件。 Header 也包含其他基础文件类型的信息,比如,目标架构,以及那些影响该文件的剩余部分的一些特定选项的标志。 紧接 Header 之后的是 Load commands ,一系列不定长的加载命令。这些加载命令具体说明了 Mach-O 文件的布局和联系特征。
-
在 Load commands 之后,是 Data 。Data 包涵一个或多个 segment ,每个 segment 包含零个或多个 section 。每个 section 包含代码或特定类型的数据。每个 segment 定义了一个虚拟内存地址偏移量的区域,从而,动态链接将其映射到进程的地址空间。
-
在用户级全链接的 Mach-O 文件中,最后一个 segment 是 link edit (链接器)段。这个段包含了链接器信息表,比如,符号表、字符串表等,被动态链接器链接到它所依赖的库的一个可执行文件或 Mach-O 文件的 bundle。 得到 Mach-O
-
查看 Segment 和 Section
可以利用 size 查看 Mach-O 文件的 Segment 和 Section
size -l -x -m MTXX |
- 查看符号表及对应的动态链接库
利用 nm 命令查看 Mach-O 的符号名
nm -nm MTXX |
以上命令的输出比较多,就不复制粘贴了。
导出头文件
结合上一篇文章的内容,导出头文件
class-dump MTXX > MTXX.h |
利用 Cycript 进行运行时分析
- 获得进程 PID
在越狱设备中开启美图秀秀,并切回到越狱设备的终端,找到美图秀秀的进程编号 PID。
NY:~ root# ps aux | grep "MTXX" |
找到 mobile 对应的 PID 949,之后利用 Cycript 进行运行时分析
- 使用 Cycript
NY:~ root# cycript -help |
可以知道只要加上 -p 选项即可进入 Cycript 的运行状态。 Cycript 换行不太方便,直接输入回车键会立即执行脚本。所以,我采用多个空格来实现换行。
- 美图秀秀运行时分析
结合已经得到的头文件,找到头文件中的类以及该类对应的方法,尝试使用 Cycript 执行这些方法。
cy# var delegate = UIApp.delegate |
在 App 的运行时,我们可以执行已有的方法,比如,在窗口上弹出一个 UIAlertView 。 再比如,从 MTXX.h 中查找到 HomeViewController 有 pullDownToCamera 的实例方法。当调用 pullDownToCamera 方法时,手机屏幕就会弹出照相机的界面。 因此,通过调用导出的头文件中方法,并根据应用运行时的表现,就可以大概想象出应用的基本结构。
Cycript 其他姿势
- 应用代理
在 Cycript 中 UIApp 与 [UIApplication sharedApplication] 作用相同
NY:~ root# cycript -p SpringBoard |
- 创建一个新的实例
var delegate = new Instance(0x148aa400) |
- 获得对象的 ivar
ivar(instance variable) 即对象的实例变量,以上面的 delegate 为例,delegate 的实例变量为
cy# var delegate = new Instance(0x148aa400) |
即,获得对象的实例变量方法是,直接输入 <*对象名> 。
- 打印对象方法
如下代码所示,第一个参数是类名
function printMethods(className, isa) { |
用法如下
cy# printMethods("NSRunLoop", true) |
- Hook 方法
系统默认的 currentRunLoop 会返回 CFRunLoop 实例的详细描述,如下所示。
cy# [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] |
将原来方法替换掉
cy# original_NSRunLoop_description = NSRunLoop.prototype['description']; |
原来的 description 方法被替换为新的描述字符串,再执行方法则会有如下输出。
cy# [NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] |
- 打印视图层级关系
递归打印视图层级关系
cy# UIApp.keyWindow.recursiveDescription().toString() |
小结
-
学习的目标规划 开端两篇文章主要学习了几个常用工具的使用,也就是方法论。然而,只懂得使用工具,是不足以学会逆向的,所以后面学习完 IDA 的使用之后,就会整理一篇理论的文章。
-
class-dump 对于某些 Swift 混编的项目,会造成 crash 的报错。比如在对天猫应用进行导出头文件的时候,就报如下错误。
➜ Reverse class-dump Tmall4iPhone > Tmall4iPhone.h |
可以继续关注原作者会否进行适配,毕竟 Swift 是发展的趋势。
- 正向开发和逆向开发的核心 从这次学习过程中,我们可以发现,逆向工程和正向工程的区别,就是二进制文件 Mach-O 文件获得方式的区别。正向开发时,是先编写程序,然后编译、链接、签名、打包最终生成含有应用 Mach-O 的包文件。而逆向开发,则是相反,首先是要先获得 Mach-O 文件,再根据二进制文件得到相应的代码,进行分析,修改等操作。
参考资料
-
Cycript 的奇淫技巧 http://iphonedevwiki.net/index.php/Cycript_Tricks
-
iOS安全–使用Cycript进行运行时分析 http://www.blogfshare.com/ioss-cycript.html
-
念茜女神的 Hack 实战——解除支付宝 App 手势解锁错误次数限制 http://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/ios-security-defense/hack-practice.html
-
iOS逆向工程(Cycript脚本语言使用与实战) http://www.jianshu.com/p/7c41b03c9eb3
-
Cycript 简介以及绕过屏幕解锁密码 http://security.ios-wiki.com/issue-4-5/ (这篇文章的无密码解锁部分已过时,所以没有介绍。里面的方法已经废除,可以通过导出头文件查看)

